Content
- 1 1. Cooling Performance
- 2 2. Use Case and Convenience
- 3 3. Capacity and Storage
- 4 4. Price
- 5 5. Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
- 6 Which One Is Right for You?
- 6.1 Go for an Ice Cooler Container If:
- 6.2 Go for a Portable Fridge If:
- 6.2.1 1. You Frequently Need to Keep Food or Drinks Cold for a Long Time
- 6.2.2 2. You Want Stable Cooling Performance and Precise Temperature Control
- 6.2.3 3. You Can Access Car Power or Other Electricity Sources and Need Continuous Cooling
- 6.2.4 4. You Need to Keep Larger Quantities of Food or Drink Cold
Ice Cooler Containers and Portable Fridges might appear to serve the same basic purpose of keeping food and beverages cool, there are significant differences between the two in terms of their design, functionality, and the specific situations they are best suited for. While both are portable cooling solutions, each offers distinct features that make them more suitable for certain types of activities or conditions. Whether you’re planning a short camping trip, a long road journey, or simply need to store cold items for a few hours, understanding these differences can help you choose the right option for your needs. From power requirements and cooling efficiency to storage capacity and price, the decision depends on your intended use, how long you’ll need cooling, and what type of convenience you’re seeking.
1. Cooling Performance
When considering coolers or portable fridges, the cooling performance plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the contents, such as food and drinks, remain at a desirable temperature over extended periods. The effectiveness of a cooler or portable fridge is influenced by its design, insulation, and cooling mechanisms. To fully understand the differences between these two types of cooling solutions, it’s important to break down their functionalities, cooling times, and power requirements.

Ice Cooler Container
Ice cooler containers are the traditional, portable solution for keeping items cool. They are commonly seen at picnics, camping trips, or outdoor events. These coolers operate through passive cooling, which means they rely on the insulation material and external cold sources like ice or ice packs to keep the internal temperature low.
Materials and Construction
Ice cooler containers are often constructed from durable materials such as hard plastic, polyethylene, or foam. These materials serve as insulating barriers that reduce the amount of heat entering the cooler and slow the transfer of heat from the outside to the inside. The better the insulation, the longer the cooler will maintain its cold temperature.
-
Foam Insulation: Foam coolers are typically lighter and more affordable. Foam has a relatively high thermal resistance, meaning it resists heat transfer effectively. However, its durability may be a concern if the cooler is subjected to rough handling.
-
Plastic or Hard Shell Insulation: More expensive models may feature thick plastic or heavy-duty hard shell construction. These coolers provide better protection from external elements like UV rays and physical impacts, making them more durable for rugged environments.
Cooling Mechanism
The cooling process of ice coolers relies primarily on the presence of ice, gel ice packs, or frozen elements placed inside the cooler. When these cooling agents are placed inside, they absorb the heat from the contents, keeping them cool for an extended period.
-
Ice: The most common cooling method is ice. Ice absorbs heat as it melts, keeping the internal temperature of the cooler low. The amount of ice used will affect how long the contents remain cool. The more ice you pack into the cooler, the longer the cooling duration.
-
Ice Packs: Some coolers are used with specially designed ice packs or gel packs. These packs can stay frozen for a long time and are reusable, making them a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional ice. Ice packs are often more efficient in terms of size-to-cooling ratio, but they require proper freezing before use.
-
Frozen Elements: Some coolers come with additional components like frozen bottles or pre-frozen water containers. These elements can keep the internal temperature of the cooler low for hours, though they typically offer shorter cooling durations than large quantities of ice.
Cooling Duration
The cooling duration of an ice cooler container varies significantly depending on several factors, including:
-
Insulation quality: High-quality foam and plastic insulation will naturally extend the cooler’s ability to maintain a cold environment.
-
Amount of ice: The more ice you add, the longer the cooling effect will last. However, the ice will eventually melt, and the contents may begin warming up after a certain period.
-
Environmental conditions: If the cooler is placed in a very hot environment or exposed to direct sunlight, the cooling duration may be reduced significantly.
Typically, an ice cooler container can keep items cold for anywhere between a few hours and up to 24 hours, depending on the factors mentioned above. Coolers that are designed for long-term use in extreme temperatures (like high-end models for hunting or fishing) may have advanced insulation and can keep ice for up to 3-5 days.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ice Cooler Containers
Advantages:
- Affordability: Ice cooler containers are relatively inexpensive compared to portable fridges.
- No need for power: As they rely on ice or ice packs, there is no need for electricity or batteries to keep the contents cool.
- Lightweight: Most ice coolers are easy to carry around, making them ideal for camping, picnics, or day trips.
Disadvantages:
- Limited cooling duration: The cooling performance is limited by the ice or ice packs, meaning the contents can warm up as the ice melts.
- Messy: Ice melts over time and can create a pool of water inside the cooler, which can lead to spills and wet items.
- Requires preparation: Ice needs to be stored or prepared in advance, which might be inconvenient for certain uses.
Portable Fridge
A portable fridge is an advanced, electric cooling solution designed to offer continuous cooling without the need for ice. These fridges often use the same cooling mechanisms as standard refrigerators and can maintain very low temperatures, even freezing contents in some cases.
Cooling Mechanism
Portable fridges operate using built-in cooling systems that are typically powered by electricity. There are two main types of cooling mechanisms used in portable fridges:
-
Compressor-based Cooling: This type of cooling system uses a compressor (similar to a car fridge or home refrigerator) to circulate refrigerant through the system. The compressor works by compressing the refrigerant, which increases its temperature, then releasing it to cool the fridge. Compressor-based cooling systems are typically more efficient and capable of reaching lower temperatures.
-
Thermoelectric Cooling: Some portable fridges use Peltier elements that create a heat difference by passing electricity through a junction of materials. While these systems are less energy-efficient than compressor systems, they are typically lighter and more affordable. However, they may not cool as effectively in very hot environments.
Power Source
Portable fridges require a constant power source to operate, which sets them apart from traditional coolers. They can be powered in several ways:
-
Car power supply (12V): Many portable fridges are designed to plug into a car’s power outlet using a 12V adapter. This makes them ideal for road trips, camping, or other travel situations where access to electrical outlets is limited.
-
Battery: Some portable fridges come with rechargeable batteries that can provide cooling for a limited time. The advantage of this is that you can take the fridge to places without a direct power source, though the cooling duration depends on the battery life.
-
Home outlet (110V/220V): Portable fridges with AC/DC power adapters can be plugged into a standard home outlet, allowing you to use them like a small refrigerator when you’re at home, in a hotel, or even at a campsite with access to power.
-
Solar Panels: Some higher-end portable fridges can be paired with solar panel systems, which allow for off-grid cooling. This is especially useful for long-term outdoor excursions or camping trips.
Cooling Duration
Unlike ice cooler containers, portable fridges can maintain their cooling effect for as long as they are powered. The ability to cool food and drinks continuously means that you don’t need to worry about melting ice or losing cooling power as time passes. This makes them highly reliable for extended use.
The cooling duration is only limited by the battery life if you are not plugged into a power source. If you’re using the fridge with a car’s 12V power supply or an external power source, the cooling can last indefinitely. Depending on the size and power efficiency, portable fridges can run continuously for days or even weeks when powered by solar panels or vehicle batteries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Portable Fridges
Advantages:
- Continuous cooling: Portable fridges can keep items cool indefinitely as long as they are powered.
- Energy-efficient: Especially the compressor-based models, portable fridges are more energy-efficient than relying on ice or ice packs.
- Versatility: They can operate on multiple power sources, including AC, DC, and batteries, making them adaptable to various situations.
Disadvantages:
- Power dependency: Unlike ice coolers, portable fridges require a continuous power supply to function, which can limit their use in remote areas without access to electricity.
- Higher initial cost: Portable fridges tend to be more expensive than traditional ice coolers, especially the compressor-based models.
- Weight and size: Depending on the model, portable fridges can be heavier and bulkier than their cooler counterparts, making them less portable.
Cooling Performance of Ice Cooler Containers vs. Portable Fridges
| Feature | Ice Cooler Container | Portable Fridge |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Ice, ice packs, frozen elements | Compressor-based or thermoelectric cooling system |
| Cooling Duration | A few hours to 1-2 days | Continuous cooling, as long as power is available |
| Power Requirement | None (requires ice) | Requires power (AC, DC, battery, or solar) |
| Temperature Range | Typically 0-15°C (32-59°F), dependent on ice amount | Can go as low as -18°C (0°F) or below with compressor |
| Maintenance | Ice replenishment required periodically | Low maintenance; requires power source |
| Portability | Lightweight and easy to transport | Bulkier and heavier, but still portable |
| Ideal Use | Short-term use, outdoor events, picnics | Long-term use, camping, road trips, outdoor work |
| Cost | Relatively inexpensive | Generally more expensive |
2. Use Case and Convenience
When deciding between an ice cooler container and a portable fridge, understanding their practical uses and convenience factors is essential. While both products are designed to keep food and drinks cool, they serve different purposes and are better suited for different types of activities. The key distinctions between them lie in their intended use, convenience, and specific features.
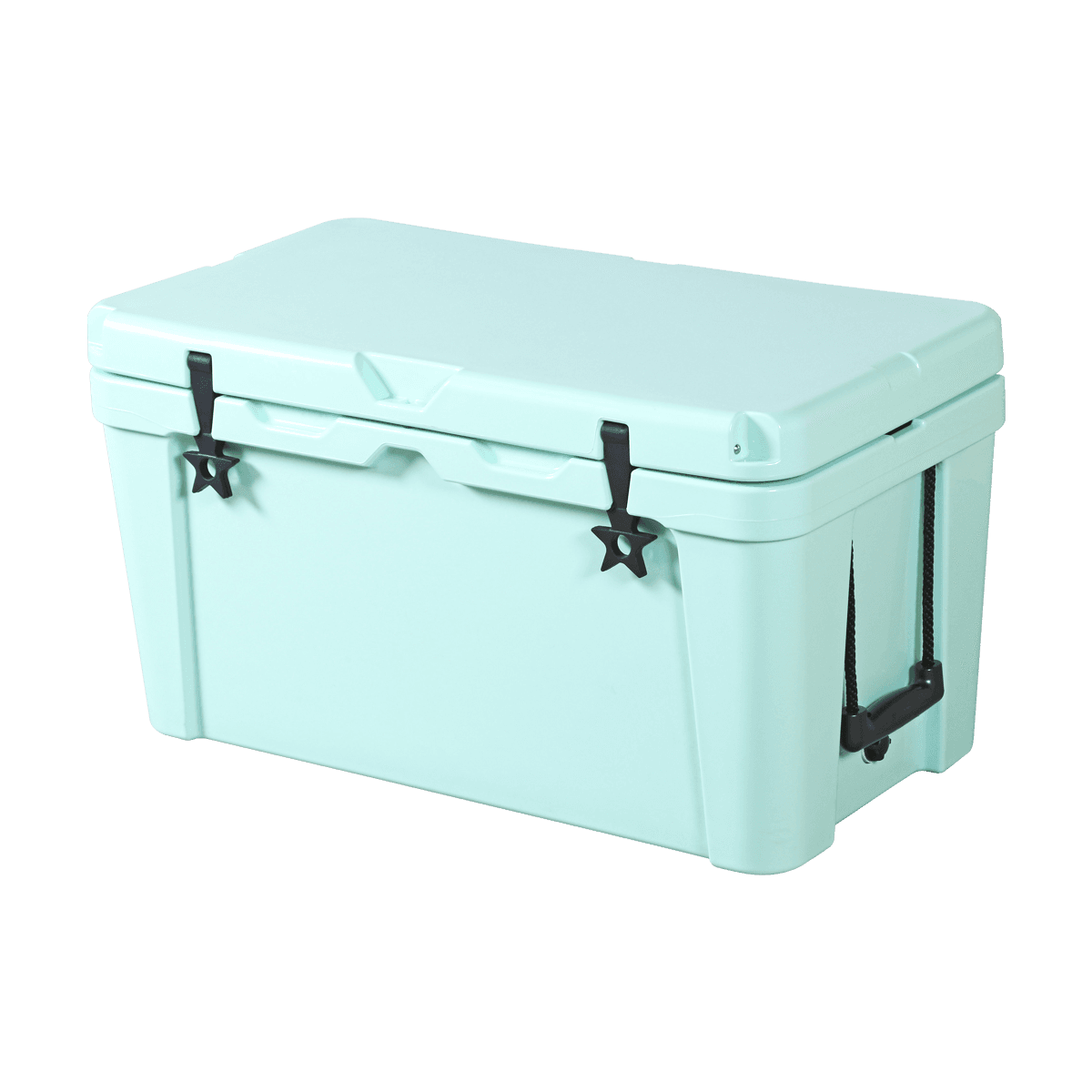

Ice Cooler Container
Ice cooler containers are primarily designed for short-term use. They are excellent for day trips or outdoor activities where you don’t need to store perishables for an extended period. Whether you’re heading to the beach, going camping for a weekend, or setting up a picnic in the park, ice coolers offer a simple and effective way to keep your food and drinks chilled without the need for electricity.
Ideal Use Cases
Ice cooler containers are ideal for short-term activities where long-lasting cooling is not required. Here are some of the key scenarios where ice coolers shine:
-
Camping: When camping for a night or two, an ice cooler is perfect for keeping drinks cold and perishable food fresh. It’s easy to pack and doesn’t require any external power source.
-
Picnics and Day Trips: For a quick trip to the beach or a picnic in the park, an ice cooler can store your food and drinks for a few hours, ensuring they stay cool for the duration of your outing.
-
Fishing: For anglers who want to keep their catch fresh until they get home, an ice cooler offers a straightforward solution. The cooler can maintain the temperature of fish and other perishable items until you’re back from your trip.
-
Outdoor Events: Whether it’s a sports event, tailgate party, or barbecue, ice coolers are great for storing drinks and food for the day, offering enough cooling to keep things fresh for several hours.
Convenience
The convenience of an ice cooler lies in its simplicity and ease of use. Here’s why:
-
No Power Required: Ice coolers are passive devices, meaning they don’t need any electricity to function. They only rely on ice or ice packs for cooling, which makes them highly portable. You can use them anywhere, even in remote locations without access to electricity or a car power source.
-
Lightweight and Easy to Transport: Ice coolers are usually lightweight, especially the smaller models. They come with handles, wheels, or straps that make them easy to carry, even over long distances. The absence of a built-in cooling system keeps their weight lower compared to portable fridges.
-
Low Maintenance: Ice coolers require minimal maintenance. All you need to do is pack them with ice or ice packs, and you’re good to go. After your trip, simply drain the water, rinse the cooler, and store it until your next outing.
-
Affordable: Ice coolers are relatively inexpensive, making them a great choice for people who only need a basic cooling solution for occasional trips. They come in various sizes and can be found at most outdoor retailers at accessible price points.
Drawbacks
Despite their many benefits, there are a few drawbacks to consider with ice coolers:
-
Limited Cooling Duration: The biggest downside of an ice cooler is its limited cooling duration. The cooling effect depends entirely on the amount of ice you use. As the ice melts, the temperature inside the cooler rises. Depending on the external temperature and the quality of the insulation, the ice might last anywhere from a few hours to a full day. If you’re heading out on a long trip or need to store food for more than a day, an ice cooler may not be sufficient.
-
Mess and Water Accumulation: Ice melts and turns into water, which can create a mess inside the cooler. Depending on what’s inside, you may end up with soggy food and drinks. Some models come with drainage plugs to help with water removal, but it still requires extra attention.
-
Requires Preparation: Ice needs to be pre-packed and kept frozen until the cooler is needed. This can be inconvenient, especially if you’re in a hurry or don’t have easy access to ice.
Portable Fridge
Portable fridges, on the other hand, offer a more long-term cooling solution. They are powered devices that utilize electricity to maintain a cold environment, and they are designed for extended use. Whether you’re embarking on a multi-day camping trip, a road trip, or need to transport refrigerated goods, portable fridges provide consistent cooling and convenience.
Ideal Use Cases
Portable fridges excel in situations where long-term, stable cooling is needed. Here are a few scenarios where a portable fridge stands out:
-
Long Road Trips: For extended travel, especially in hot climates, portable fridges are essential. They keep your food and beverages chilled for days, which is perfect for long road trips, camping in remote locations, or cross-country drives. Since they operate on electricity, they can cool items for an indefinite period as long as power is available.
-
Extended Camping: When you plan to camp for a week or more, a portable fridge provides consistent cooling for meats, dairy products, and other perishable foods. It ensures your supplies stay fresh throughout your trip.
-
Food Transport: Portable fridges are also used for transporting refrigerated goods, such as groceries, medication (e.g., insulin), or beverages. Whether you’re transporting perishables for a catering event or keeping supplies for a remote project, portable fridges can maintain a reliable cold chain.
-
Off-Grid Adventures: If you’re going off the grid, a portable fridge that works with solar power or a rechargeable battery can be a game-changer. This is especially useful for remote camping, overlanding, or survivalist expeditions, where access to traditional power sources is limited.
Convenience
The convenience of a portable fridge lies in its ability to provide constant cooling without the need to replenish ice or worry about items warming up. Here’s how it excels:
-
Continuous Cooling: Unlike ice coolers, portable fridges can cool food for days without the need for ice. Whether you’re plugged into your car’s 12V power supply, using a rechargeable battery, or hooking it up to a solar panel, a portable fridge can maintain a steady temperature for as long as you need it to.
-
Stable Temperature: Portable fridges provide consistent cooling, which is especially important for storing perishable food items like meats and dairy. Since they rely on compressors (in most models), they can maintain a lower and more stable temperature, even when the outside temperature fluctuates. This makes portable fridges better for long-term storage compared to ice coolers.
-
Multiple Power Sources: One of the biggest advantages of portable fridges is their versatility when it comes to power sources. You can run them off a car’s 12V outlet, use them with an AC adapter in your home or hotel, or even rely on solar panels and rechargeable batteries for off-grid use. This flexibility makes them suitable for a range of activities.
-
Temperature Control: Many portable fridges come with built-in thermostats and temperature controls, allowing you to adjust the cooling to suit your needs. You can set the fridge to a specific temperature, and it will maintain that temperature continuously. This is particularly useful for delicate items like fresh produce or medicines.
-
Portability: While portable fridges are generally heavier than ice coolers due to the built-in cooling system, many models come with wheels or handles for easier transportation. Some are designed to fit into the trunk of a car, making them ideal for road trips and outdoor adventures.
Drawbacks
Despite their many advantages, portable fridges also come with some disadvantages:
-
Higher Initial Cost: Portable fridges are more expensive than ice coolers, particularly the models with compressors. The price reflects the advanced technology, but it can be a significant investment, especially for occasional users.
-
Heavier and Bulkier: Portable fridges tend to be bulkier and heavier than ice coolers due to the cooling components. This can make them less convenient to carry over long distances or in tight spaces.
-
Power Dependency: While portable fridges are versatile in terms of power sources, they are still dependent on electricity to function. If you’re in a remote area without access to power or if your battery runs out, the fridge will stop working, and your food could spoil.
Use Case and Convenience
| Feature | Ice Cooler Container | Portable Fridge |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal Use Case | Short-term activities (camping, picnics, fishing) | Long-term use (road trips, extended camping, food transport) |
| Cooling Duration | A few hours to a day | Continuous, as long as powered |
| Power Requirement | No power required (uses ice) | Requires electricity (12V, AC, battery, or solar) |
| Portability | Lightweight, easy to carry | Heavier but still portable (with wheels/handles) |
| Temperature Stability | Cooling lasts until ice melts | Stable temperature maintained over long periods |
| Convenience | Low-maintenance, no setup required | Requires power but provides consistent cooling |
| Cost | Inexpensive, budget-friendly | More expensive, higher upfront cost |
3. Capacity and Storage
When comparing ice cooler containers and portable fridges, one of the most important factors to consider is their capacity and storage efficiency. Both options offer different solutions for storing food and beverages, but their design and functionality can affect the overall storage experience. The capacity and the way each system maintains temperature are central to their effectiveness and suitability for different situations.
Ice Cooler Container
Ice cooler containers are known for their large capacity and simple design, which makes them ideal for storing large quantities of food and drinks. They are perfect for short-term use where you need to store a lot of items, but their storage efficiency can be less than that of a portable fridge due to the reliance on ice.
Capacity and Storage Space
The capacity of an ice cooler container can vary widely depending on the model. These coolers are generally designed to hold large quantities of food, drinks, and other items, making them a great choice for group outings, family camping trips, or events where a significant amount of food and beverages need to be stored. The volume of an ice cooler can range from small, portable models with a 10-20 liter capacity to large coolers with capacities of 100 liters or more.
-
Larger Capacity: Ice coolers typically offer more space for storage compared to portable fridges. Since they do not have any built-in cooling mechanisms, the lack of an internal system frees up more room for actual contents. This makes them suitable for storing bulkier items, such as whole fruits, large packs of drinks, frozen meats, and snacks.
-
Flexible Storage Options: The large storage capacity also allows you to use customized inserts (such as ice packs or dividers) to organize the cooler better. Although they might not have internal shelves or compartments like a fridge, these coolers can be easily packed with a wide variety of items, depending on how you want to arrange them.
Cooling Efficiency and Temperature Uniformity
While ice coolers offer more space, cooling efficiency can become a limitation. Since these coolers rely on ice to cool their contents, the distribution of cold is not uniform. Here are the factors that affect cooling efficiency:
-
Ice Distribution: The cold from the ice tends to be concentrated near the ice blocks or packs, while the rest of the cooler might not be as cool. This means that food or drinks placed at the top or bottom of the cooler may not be kept at the optimal temperature, especially if the ice begins to melt. The lack of a controlled cooling system can result in uneven temperature distribution.
-
Melting Ice: As the ice melts, the cooling effect diminishes, and the temperature inside the cooler rises. After the ice melts completely, the cooler no longer provides a cold environment unless more ice is added. This can be problematic if you need to store items for long periods or in warm conditions.
-
Limited Control: Unlike portable fridges, ice coolers do not offer any form of temperature control. You rely entirely on the quantity of ice and the external temperature to maintain a cool environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Storage in Ice Cooler Containers
Advantages:
- Large Capacity: Ice coolers often provide more space for storing a wide range of food and beverages.
- Affordable: They are generally less expensive than portable fridges, and their larger capacity means you get more value for your money.
- Simple to Use: With no need for power sources, ice coolers are easy to use, and you don’t have to worry about managing settings or power supply.
Disadvantages:
- Inefficient Use of Space: Ice coolers can be less efficient in terms of storage optimization since ice occupies a significant portion of the space. This means less room for actual items you want to store.
- Uneven Cooling: The lack of a cooling system leads to uneven temperature distribution, especially as the ice melts.
- Limited Duration: The cooling effect only lasts as long as the ice, so after it melts, you need to add more ice or the cooler becomes ineffective.
Portable Fridge
In contrast to ice coolers, portable fridges tend to have smaller capacities, but they offer better storage efficiency and temperature control. These fridges are designed to store food at specific temperatures, making them ideal for preserving perishables over extended periods.
Capacity and Storage Space
Although portable fridges generally have smaller capacities than ice coolers, they are designed to store food and beverages more efficiently. The average capacity of a portable fridge ranges from 20 liters for compact models to 50-80 liters for larger ones. However, they often make better use of available space, thanks to their built-in cooling systems.
-
Optimized Storage: Unlike ice coolers, which leave gaps for ice to take up space, portable fridges are designed with internal compartments, shelves, and drawers that make the most out of the available space. This allows for better organization of food and drinks, making it easier to store items of different sizes.
-
Temperature Zones: Many portable fridges feature separate compartments that can maintain different temperatures. For example, one section can be set to a freezing temperature for ice cream or meat, while the other can be set to refrigerate beverages and produce. This makes portable fridges much more versatile in terms of storage.
Cooling Efficiency and Temperature Control
One of the major advantages of a portable fridge over an ice cooler is the ability to maintain a consistent and controlled temperature. Since portable fridges come with a built-in cooling system, they are far more efficient at keeping everything within a stable temperature range.
-
Consistent Temperature: A portable fridge can keep its contents at a consistent temperature, usually between -18°C (0°F) to 10°C (50°F), depending on the model and settings. This ensures that food, beverages, and other items are kept at optimal temperatures, reducing the risk of spoilage and preserving freshness.
-
Adjustable Settings: Many portable fridges come with digital or analog thermostats that allow you to set a precise temperature. This is particularly useful for perishable items that require specific cooling conditions, such as dairy, meat, or certain medications.
-
Efficient Use of Space: With a cooling system integrated into the fridge, there is no need for ice, which means you can make better use of the entire storage space. The contents are kept cold uniformly, and there are no large blocks of ice taking up valuable room.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Storage in Portable Fridges
Advantages:
- Efficient Use of Space: Portable fridges offer better organization and space optimization than ice coolers. With dedicated compartments and shelves, the available space is used more effectively.
- Precise Temperature Control: With adjustable temperature settings, you can maintain the exact temperature needed for different types of food and beverages.
- Consistent Cooling: Portable fridges provide a more consistent cooling effect, preventing food from warming up in places where there’s no ice.
- No Ice Needed: Unlike ice coolers, portable fridges don’t require ice, which frees up more room for food storage and eliminates the mess of melting ice.
Disadvantages:
- Smaller Capacity: Portable fridges usually have a smaller capacity than ice coolers, which can limit the amount of food and drinks you can store. While you can still store a decent amount, it might not be enough for large groups or extended trips.
- Higher Cost: The technology involved in portable fridges means they are generally more expensive than ice coolers. The initial investment can be significant, especially for high-end models with advanced features.
- Power Requirement: Portable fridges require a power source to operate, meaning you need access to a 12V car outlet, an AC power supply, or a battery pack. This limits their use in remote areas without a power source.
Capacity and Storage Efficiency
| Feature | Ice Cooler Container | Portable Fridge |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Larger capacity, ideal for bulk storage | Smaller capacity, better for organized storage |
| Storage Efficiency | Less efficient due to ice taking up space | More efficient use of space with compartments |
| Temperature Control | No temperature control, cooling relies on ice | Precise temperature control with adjustable settings |
| Cooling Consistency | Uneven cooling, especially as ice melts | Consistent cooling throughout the fridge |
| Storage Flexibility | Can store a variety of items, but ice limits space | Can store different types of items with specific temperature zones |
| Ideal Use | Short-term trips, large group outings | Long-term use, food preservation, and perishables |
| Cost | Affordable, budget-friendly | More expensive due to built-in cooling system |
4. Price
When considering an ice cooler container versus a portable fridge, the price is one of the most significant factors that can influence your decision. Each option caters to different needs, and the price varies substantially depending on features, size, and technology involved.
Ice Cooler Container Pricing
Ice cooler containers, also known as coolers, are a popular choice for those who need a reliable and simple solution to keep food and beverages cold for a short period. These coolers come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and designs, and their pricing generally reflects the level of insulation, material quality, and brand name. The price range for ice cooler containers is quite broad, making them accessible for nearly every budget.
Basic Ice Cooler Containers
Basic coolers, which are primarily made of plastic or lightweight materials, tend to be the most affordable options. These models rely on simple ice packs or ice cubes to keep their contents cold. A small to medium-sized cooler, which can hold up to 30 liters, might cost anywhere from $20 to $50. These are perfect for day trips, picnics, or short-term use. Their basic design is cost-effective and practical for people who don’t require advanced cooling capabilities.
Mid-Range Ice Cooler Containers
Mid-range coolers come with improved insulation materials, which allow them to maintain cooler temperatures for longer periods. These containers can range in price from $50 to $150 depending on the brand, size, and features such as built-in cup holders, better sealing, and reinforced exteriors for durability. Many of these models are marketed as being able to keep contents cold for several days, making them ideal for weekend trips, camping, or extended outdoor events.
Premium Ice Cooler Containers
At the higher end of the market, premium coolers offer top-of-the-line performance with exceptional insulation that can keep ice frozen for up to a week or more. These coolers are often made of heavy-duty materials, including roto-molded plastic or metal, and come equipped with advanced features such as built-in bottle openers, ergonomic handles, and even advanced drainage systems for easier cleaning. Prices for these high-end coolers typically range from $150 to $400 or more, with some models pushing higher based on brand reputation (e.g., YETI, Pelican). These coolers are perfect for serious outdoor enthusiasts or those who need high performance in extreme conditions.
Overall Ice Cooler Container Value
The ice cooler container is generally a more affordable option compared to portable fridges. The key here is that coolers do not rely on electrical power or sophisticated cooling systems. They are designed to work with ice or cold packs, which limits their functionality but also keeps costs low. For casual users who don’t need long-term refrigeration, coolers provide excellent value for money. However, the cost can increase significantly as the size and quality of the cooler rise.
Portable Fridge Pricing
Portable fridges, on the other hand, offer a more advanced solution for cooling needs. Unlike ice cooler containers, portable fridges use built-in refrigeration systems, making them more versatile and capable of cooling to a wide range of temperatures. However, this technology comes at a higher price point.
Basic Portable Fridges
Even the most basic portable fridges, which might only offer a few cooling settings and small capacity, can be quite expensive compared to a basic cooler. Prices for entry-level models typically range from $100 to $250. These portable fridges usually offer more convenience than a cooler, as they are powered by electricity and don’t require ice. However, they may not have the same level of efficiency or advanced features as their higher-end counterparts.
Mid-Range Portable Fridges
Mid-range portable fridges provide more storage space, better insulation, and more cooling options. They are often designed to handle more demanding applications, such as longer trips or more extended outdoor events. Prices for these fridges typically range from $250 to $500. In this price range, you can expect features such as dual-zone cooling, digital temperature controls, and better energy efficiency, which are ideal for users who want both reliability and flexibility.
Premium Portable Fridges
Premium portable fridges are highly advanced models that can function as both a refrigerator and a freezer. These fridges are designed for serious outdoor use, road trips, RVs, and camping. Prices for premium portable fridges usually start at $500 and can reach as high as $1,500 or more, depending on the brand, size, and features. For this price, you will get models that can operate in extremely hot or cold temperatures, have advanced energy-saving technologies, and offer massive storage capacities (e.g., 100 liters or more). Some models come with additional features such as solar panel compatibility, built-in wifi, and apps for remote control.
Overall Portable Fridge Value
Portable fridges are an investment, and their cost reflects the technology and features they offer. Unlike coolers, which rely on ice, portable fridges can run continuously and maintain consistent temperatures, making them more versatile for various applications. The prices can be steep, but for those who need reliable cooling without the hassle of replenishing ice, a portable fridge is a worthwhile investment. However, the high initial cost and ongoing power requirements should be carefully considered.
Ice Cooler vs. Portable Fridge
| Product | Price Range | Cooling Technology | Duration of Cooling | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Ice Cooler Container | $20 - $50 | Ice Packs or Ice Cubes | A few hours to a day | Short-term use (picnics, day trips) |
| Mid-Range Ice Cooler | $50 - $150 | Enhanced Insulation | 2-5 days | Weekend trips, camping |
| Premium Ice Cooler | $150 - $400+ | High-Performance Insulation | 5-7 days or more | Extended outdoor trips, expeditions |
| Basic Portable Fridge | $100 - $250 | Refrigeration System (Electric) | Continuous cooling (varies) | Short-term and mid-term use |
| Mid-Range Portable Fridge | $250 - $500 | Dual-Zone Refrigeration | Continuous cooling (varies) | Road trips, RVs, longer camping |
| Premium Portable Fridge | $500 - $1,500+ | Advanced Cooling & Freezing | Continuous cooling (varies) | Extended travel, RVs, off-grid use |
Long-Term Cost Considerations
While the upfront cost of a portable fridge is generally higher, it is important to consider the long-term costs. An ice cooler requires ice or cold packs, which can add to the overall cost over time, especially if the cooler is used frequently. For a portable fridge, the primary ongoing cost is electricity, which can vary depending on the energy efficiency of the unit and how often it is used.
Additionally, portable fridges may require maintenance, such as cleaning the cooling system or replacing seals. In contrast, ice coolers are largely maintenance-free apart from occasional cleaning and checking for wear and tear.
5. Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
When choosing between an ice cooler container and a portable fridge, energy consumption and environmental impact are critical considerations, especially as sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor for consumers.
Ice Cooler Container: No Power Needed, More Eco-Friendly
Ice cooler containers have a significant advantage in terms of energy consumption and environmental impact. As simple, passive cooling systems, coolers do not require any electricity to function, making them a more environmentally friendly choice in many respects.
Energy Consumption
The fundamental principle behind an ice cooler container is its reliance on ice or cold packs to maintain low temperatures. Ice coolers operate entirely through thermal insulation, which helps preserve the cold temperature for a certain period. Since these coolers do not require electricity to run, they are extremely energy-efficient. The only external input needed is the ice itself, which can be replenished at your local store or made at home.
Because ice coolers do not use power, they do not contribute to energy consumption, making them an excellent choice for energy-conscious individuals or those trying to reduce their carbon footprint. Whether you are out camping or on a day trip, the cooler’s reliance on ice rather than electricity reduces the strain on your energy resources. For this reason, ice coolers are the most energy-efficient option, especially for short-term or occasional cooling needs.
Environmental Impact
From an environmental perspective, ice coolers tend to have a much smaller ecological footprint compared to portable fridges. There are several key factors contributing to this reduced environmental impact:
-
No Need for Electricity: Since ice coolers don’t use power, they eliminate the need for electricity generation, which often relies on fossil fuels in many parts of the world.
-
Material Impact: The materials used in cooler construction, typically plastic, metal, or foam, are generally less resource-intensive than the components found in portable fridges, such as compressors and refrigeration systems. While certain high-end coolers may use more durable materials, they generally require less energy and fewer resources to manufacture.
-
Disposal: Coolers, being simpler in design, are often easier to repair and maintain, extending their life cycle and reducing waste. Many coolers can last for years, provided they are well taken care of. Even at the end of their lifespan, many cooler materials can be recycled, making them a more environmentally sustainable product overall.
However, one potential environmental drawback is the use of ice. Making ice requires energy, especially if you are using an electric freezer to create it. The more ice you need for your cooler, the higher the energy cost becomes, but this is still generally much lower than the energy used by a portable fridge.
Limited Impact in Extreme Conditions
Ice coolers are highly efficient for short-term use, but they do have limitations in extreme conditions. For example, in very hot climates, ice will melt more quickly, reducing the cooler’s effectiveness. However, this is generally a minor drawback, especially when compared to the environmental and energy costs of portable fridges.
Portable Fridge: Requires Electricity, Higher Power Consumption
Portable fridges, while offering more convenience and versatility than ice coolers, come with higher energy consumption and environmental impacts due to the need for electricity to power the refrigeration system.
Energy Consumption
Portable fridges typically require electricity to operate, and their energy consumption can vary greatly depending on several factors:
-
Size of the Unit: Larger portable fridges will naturally consume more power because they have larger cooling capacities. For example, a 40-liter fridge will use less energy than an 80-liter fridge.
-
Cooling Efficiency: Not all portable fridges are equally efficient. High-quality, energy-efficient models tend to consume less electricity compared to cheaper models. Refrigerators with digital temperature controls, insulation, and low-power compressors will generally use less energy.
-
Ambient Temperature: The outside environment plays a significant role in energy consumption. If you’re using the portable fridge in a hot climate, the fridge will have to work harder to keep the internal temperature down, resulting in higher power consumption. Conversely, in cooler conditions, the fridge will use less energy to maintain the set temperature.
-
Usage Pattern: Continuous use of the portable fridge, particularly over long periods, will increase power consumption. The more often the fridge has to run its compressor to keep the temperature down, the more electricity it will consume. This is especially true if you are using it in an off-grid scenario where the fridge is running 24/7.
Power Source and Battery Capacity
Portable fridges often need a reliable power source to function. In most cases, these fridges are powered by either a vehicle’s battery, solar panels, or an external power bank.
-
Vehicle Battery: Many portable fridges are designed to be plugged into a car or truck. While this is an easy and convenient solution for people on the go, it can drain the vehicle’s battery if the fridge is left running for extended periods without the engine running. In these cases, the fridge may require recharging the car battery or using a supplementary power system, which can be less efficient and more costly in terms of fuel.
-
Solar Power: Some portable fridges are designed to be compatible with solar panels, which is an energy-efficient solution for off-grid situations. However, solar panels themselves require an initial investment, and the amount of energy generated depends on weather conditions and sunlight exposure. This makes solar power a less reliable option unless you have the right setup.
-
External Battery Packs: For those who want to avoid the need for a vehicle, portable battery packs are another option. These can be useful for camping, hiking, or off-grid living. However, they still require charging and may need to be recharged after only a few hours or days of use, depending on the size and capacity of the battery pack.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of portable fridges is more complex than that of ice coolers. While these fridges are undoubtedly more convenient, their reliance on electricity means they contribute to the carbon footprint of electricity generation. In many parts of the world, electricity is still primarily generated from fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas. This means that every hour the fridge operates consumes energy and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the production of portable fridges is more resource-intensive due to the components involved, such as compressors, motors, and electronic parts. The environmental impact of manufacturing portable fridges is much higher than that of a simple cooler. Additionally, portable fridges may have a shorter lifespan due to wear and tear on the compressor, which can make them less sustainable in the long run.
Lastly, the disposal of portable fridges can be problematic. Many of the components in a portable fridge, such as refrigerants and electronic parts, are not easily recyclable and can contribute to pollution if not disposed of properly.
Which One Is Right for You?
When deciding between an ice cooler container and a portable fridge, it’s important to consider your specific needs, usage patterns, and budget. Both options serve the same fundamental purpose—keeping food and drinks cold—but they do so in very different ways and come with distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Go for an Ice Cooler Container If:
Ice cooler containers are a fantastic choice for those looking for a simple, low-maintenance solution for keeping items cold. Below are some situations in which an ice cooler would be the better option.
1. You Only Occasionally Need to Keep Drinks and Food Cold
If you’re someone who only occasionally needs to store food or beverages at a cold temperature, an ice cooler is likely the most practical and economical option. Whether you’re going on a picnic, attending a barbecue, or embarking on a short camping trip, an ice cooler will keep your items cold for the duration of your outing without the need for complex setups or expensive equipment.
For example, if you’re planning a day trip to the beach, a hike, or just a short family outing, you probably won’t need a device that runs on electricity or requires constant monitoring. An ice cooler, especially the basic or mid-range models, is ideal in these situations. You simply pack the cooler with ice, load it up with your food and drinks, and you’re good to go.
2. You’re on a Budget or Don’t Want to Rely on Electricity
One of the most appealing aspects of ice cooler containers is their affordability. Whether you’re trying to keep costs down or don’t want to make a big investment in a more complex product, ice coolers are an excellent option. Basic models can cost as little as $20 to $50, making them accessible to almost anyone, especially if you’re not looking to use them frequently or for extended periods.
electricity-free operation is a big advantage if you’re trying to avoid ongoing costs or don’t have reliable access to a power source. Ice coolers do not rely on electricity, which means there’s no need to worry about battery life, charging or high energy bills. For off-grid situations or outdoor activities like camping, where access to electricity may be limited, an ice cooler container is an easy and affordable way to keep your items cold.
3. You’re Looking for Something Lightweight and Simple for Short-Term Use
If your priority is ease of use and portability, ice coolers are your best bet. These containers are generally lightweight, especially when compared to portable fridges, which often come with heavier components such as compressors and insulation systems. This makes coolers easy to transport for short-term use.
An ice cooler’s simple design and minimal setup make it perfect for quick, no-fuss use. You can throw a cooler in the back of your car, toss in some ice and snacks, and you’re ready for the day. Whether you’re going on a road trip, a picnic in the park, or a weekend camping trip, the ice cooler will provide the cooling you need without the added complexity.
4. You Don’t Mind Replenishing Ice
A significant trade-off when choosing an ice cooler container is that it requires ice, which can melt and need to be replenished. However, if you’re only using the cooler for short trips, this is usually not an issue. For example, during a day at the beach or a weekend camping trip, it’s likely you won’t need to replenish the ice frequently. As long as you plan accordingly and pack enough ice, an ice cooler can keep your contents cold for the duration of the trip.
While you may need to add more ice on particularly hot days, this process is relatively simple and doesn’t involve the complexities of maintaining a portable fridge, which would require electricity and could consume more power in these conditions.
Go for a Portable Fridge If:
Portable fridges are better suited for people who have more frequent or long-term cooling needs and are willing to make the investment in a more advanced and versatile solution. Below are some situations where a portable fridge would be the right choice for you.
1. You Frequently Need to Keep Food or Drinks Cold for a Long Time
If you find yourself regularly in situations where you need to keep food or drinks cold for extended periods—such as during long road trips, extended camping trips, or outdoor work—a portable fridge is far more convenient than an ice cooler. Ice will eventually melt, and replenishing it regularly can be cumbersome, especially on longer trips.
For example, on a week-long camping trip or cross-country road trip, you would benefit from the continuous cooling power of a portable fridge. It will keep your perishables cold or frozen for as long as you need, without the hassle of replenishing ice. This makes portable fridges an excellent choice for long-duration events where maintaining temperature stability is important.
2. You Want Stable Cooling Performance and Precise Temperature Control
Portable fridges provide consistent cooling performance that ice coolers simply can’t match. With a built-in refrigeration system, portable fridges can maintain a precise temperature (from freezing to cooling), ensuring your food stays at the desired temperature. Whether you need to freeze meat for an extended camping trip or keep beverages chilled for several days, portable fridges provide a level of temperature control that is simply impossible with ice coolers.
For people who need to store medications or specialty foods that must remain at a consistent temperature, portable fridges are the way to go. Some models even come with dual-zone cooling, allowing you to keep some items frozen while others stay chilled. This added versatility makes portable fridges more suitable for complex cooling needs.
3. You Can Access Car Power or Other Electricity Sources and Need Continuous Cooling
If you have access to a reliable power source, such as a car battery, solar panels, or an external power bank, a portable fridge becomes an incredibly convenient option. Unlike ice coolers, which require ice to function, portable fridges can operate continuously for days, making them ideal for off-grid living, RV trips, or extended outdoor adventures.
For example, if you’re traveling in an RV or van, having a portable fridge allows you to store and keep fresh food without the need to go to a grocery store every few days. As long as you have access to electricity, you won’t need to worry about your food spoiling or ice melting. Many portable fridges are designed to work seamlessly with solar panels, so if you’re planning to travel long distances or live off the grid, this is a great solution.
4. You Need to Keep Larger Quantities of Food or Drink Cold
Portable fridges come in various sizes, some capable of holding up to 100 liters or more. This makes them ideal for larger groups, extended trips, or situations where you need to store more than just a few beverages and snacks. Whether you’re catering a party, organizing a multi-day event, or going on an extended camping trip with a large group, portable fridges allow you to store a significant amount of food and drinks at optimal temperatures.
In contrast, ice coolers can only hold a limited amount of food and will need frequent replenishing of ice if you’re storing large quantities or trying to keep items cold for multiple days.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体
-4.png)
-4.png)
-2.png)
-2.png)
-2.png)



