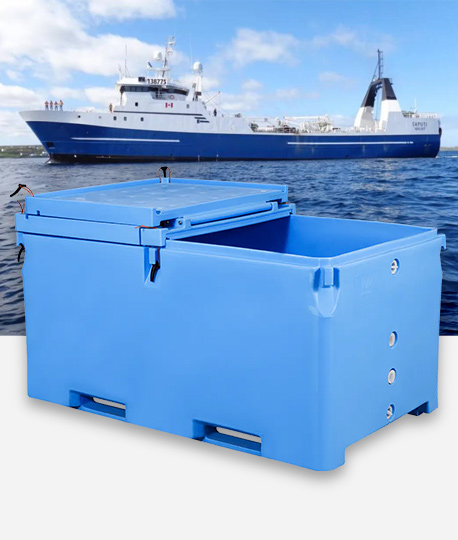
Cold chain containers are a type of containerized equipment specifically used in cold chain transportation systems. They have functions such as insulation, refrigeration, and temperature control, and can maintain the low or constant temperature environment required for goods throughout the entire logistics transportation process. With the increasing global requirements for food safety, drug effectiveness, and stability of biological products, cold chain containers are becoming an indispensable and important part of modern logistics.
The structure of cold chain containers usually includes an efficient insulation layer, a built-in or external temperature control system, a real-time temperature and humidity monitoring device, and data recording and transmission equipment. They can keep the temperature inside the container constant in extreme weather environments, thereby ensuring that the goods will not deteriorate or fail due to temperature fluctuations during transportation. For example, when transporting vaccines, plasma, precision biological reagents, or frozen foods, if there is a lack of reliable cold chain equipment support, even if the transportation time is short, the goods may face irreversible quality losses.
In logistics transportation, the application of cold chain containers not only improves transportation efficiency, but also greatly expands the circulation radius of goods. In the past, many perishable items could only be sold locally. Now, relying on the powerful preservation ability of cold chain containers, fruits, vegetables, seafood, dairy products and even high-end medicines can be transported from one country across thousands of kilometers to end consumers in another country, and still maintain their original quality. This not only drives the development of international trade, but also greatly enriches the supply of goods in local markets.
During transportation, the cold chain container is not just a "box", it is more like a movable miniature cold storage with flexible power docking methods, including connecting the power supply system of the transport vehicle, the shore power of the terminal, and even bringing its own battery to ensure continuous refrigeration throughout the transportation and loading and unloading process. Modern cold chain containers are often equipped with intelligent monitoring systems that can record temperature changes in real time and upload data remotely through the cloud platform. Once the temperature is abnormal, the system will automatically issue an alarm to remind the operator to deal with it in time to prevent damage to the goods.
From the perspective of application areas, cold chain containers cover almost all industries that are sensitive to temperature. The food sector is particularly dependent on cold chain transportation, such as meat, aquatic products, dairy products, and fresh fruits and vegetables. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is even more indispensable, especially when transporting vaccines, insulin, biological reagents, and some blood products. Any temperature control error may cause serious consequences. During the COVID-19 pandemic, cold chain containers played a key role in global vaccine transportation. Many mRNA vaccines need to be transported and stored in an ultra-low temperature environment of -70°C. Only professional ultra-low temperature cold chain containers can meet this technical requirement.
Although the role of cold chain containers in logistics is becoming increasingly important, its development also faces many challenges. The first is the high equipment cost and operation and maintenance costs, and the second is the dependence of the refrigeration system on energy, especially in remote areas or in the event of power outages during transportation, a complete backup plan is needed. The impact of traditional refrigerants on the environment has also prompted the industry to develop in a more green and environmentally friendly direction. More and more manufacturers are beginning to adopt new low-carbon, fluorine-free refrigeration technologies.
The technology of cold chain containers will develop towards intelligence, modularization, and greening. In terms of intelligence, future cold chain containers will be widely connected to the Internet of Things, achieving transparent and traceable temperature control data from warehousing to distribution; in terms of modularity, companies can flexibly combine capacity and adjust temperature ranges according to transportation needs; and the green trend will drive cold chain equipment to use more efficient and energy-saving compression systems and pollution-free refrigerants to reduce the impact on the environment.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体
-4.png)
-4.png)
-2.png)
-2.png)
-2.png)




